Trading financial markets offers multiple pathways to potential profitability, with forex and futures representing two of the most popular vehicles for traders worldwide.
Understanding the fundamental differences between these markets is essential for traders deciding where to focus their efforts.
This comprehensive comparison explores the unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges of both forex and futures trading, with insights into how proprietary trading firms like TX3 Funding are creating new opportunities in the futures space.
Understanding Forex Trading
Forex (foreign exchange) trading involves buying and selling currency pairs in a decentralized global marketplace. This market facilitates the exchange of currencies for international trade and investment, with daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion.
The Structure of Forex Markets
Unlike centralized exchanges, forex trading occurs via an electronic network of banks, brokers, and individual traders. This decentralized nature means there's no single exchange controlling currency prices. Instead, prices are determined by bid and ask quotes from multiple liquidity providers.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, following the sun around the globe through major financial centers in London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. This continuous operation allows traders to react to global events and economic data releases regardless of their time zone.
Currency pairs are categorized into majors (like EUR/USD, USD/JPY), minors (like EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD), and exotics (like USD/TRY, EUR/ZAR). Each currency pair exhibits unique characteristics in terms of volatility, liquidity, and correlation with economic factors.
Key Advantages of Forex Trading
Forex markets offer several distinct advantages that have contributed to their popularity:
Accessibility and Low Entry Barriers: Forex trading typically requires less capital to start compared to many other markets. Brokers often offer micro and mini lots, allowing traders to control positions with relatively small account sizes.
High Liquidity: Major currency pairs are incredibly liquid, which means trades can be executed quickly and with minimal slippage, even for substantial position sizes.
Leverage Availability: Forex brokers typically offer higher leverage than what's available in other markets, sometimes exceeding 100:1 in certain jurisdictions. This allows traders to control larger positions with relatively small capital, though it also amplifies risk.
Diverse Trading Strategies: The forex market accommodates various trading approaches, from scalping and day trading to swing and position trading, giving traders flexibility in how they approach the market.
Challenges in Forex Trading
Despite its advantages, forex trading presents distinct challenges:
Broker-Dependent Execution: Since there's no centralized exchange, trade execution quality can vary significantly between brokers. Some operate as market makers, potentially creating conflicts of interest.
Regulatory Variance: Forex brokers operate under different regulatory frameworks depending on their jurisdiction, leading to inconsistent levels of trader protection across the industry.
Spread and Commission Structures: Cost structures can be complex and variable, with some brokers offering commission-free trading but wider spreads, while others charge commissions with tighter spreads.
Market Manipulation Concerns: The decentralized nature of forex can sometimes lead to price spikes and manipulation, particularly in less liquid currency pairs or during major news events.
What is Futures Trading?
Futures trading involves standardized contracts to buy or sell specific quantities of an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a future date. Originally developed for agricultural commodities, futures now cover a wide range of assets including stock indices, energy products, metals, and currencies.
The Structure of Futures Markets
Futures contracts trade on centralized exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), and CBOT (Chicago Board of Trade). These exchanges provide standardization, transparency, and regulatory oversight.
Each futures contract specifies exact delivery terms: the quantity and quality of the underlying asset, delivery date, delivery location, and pricing conventions. This standardization ensures all market participants trade on equal terms.
Unlike the 24-hour forex market, futures markets operate during specific exchange hours, although many major futures contracts offer extended electronic trading hours beyond the traditional floor trading sessions.
Key Advantages of Futures Trading
Futures markets offer several compelling advantages for serious traders. We will highlight some of it here:
Centralized Price Discovery: With all trades routed through a central exchange, futures markets provide transparent price discovery and a verifiable audit trail for all transactions.
Regulatory Oversight: Futures exchanges operate under strict regulatory frameworks like the CFTC in the US, providing significant trader protections and market integrity safeguards.
Direct Market Access: Traders can access the actual exchange order book, seeing the full depth of market with visibility into limit orders and trading volume.
Diverse Asset Exposure: Futures allow traders to access a wide variety of markets in a single account - from stock indices like the S&P 500 to commodities like gold, crude oil, and agricultural products.
Lower Counterparty Risk: The exchange clearinghouse acts as the counterparty to all trades, substantially reducing the risk of default compared to some over-the-counter markets.
Challenges in Futures Trading
Futures trading comes with its own set of challenges:
Higher Capital Requirements: Traditional futures contracts often require substantial margin deposits, though micro contracts have made these markets more accessible.
Contract Expiration: Futures contracts have expiration dates, requiring traders to roll positions forward to maintain exposure beyond the current contract's expiration.
Fixed Contract Specifications: The standardized nature of futures means traders must work with fixed contract sizes, which can sometimes be too large for smaller accounts.
Limited Trading Hours: Despite extended electronic sessions, futures markets still have defined trading hours unlike the continuous forex market.
Direct Comparison: Forex vs. Futures
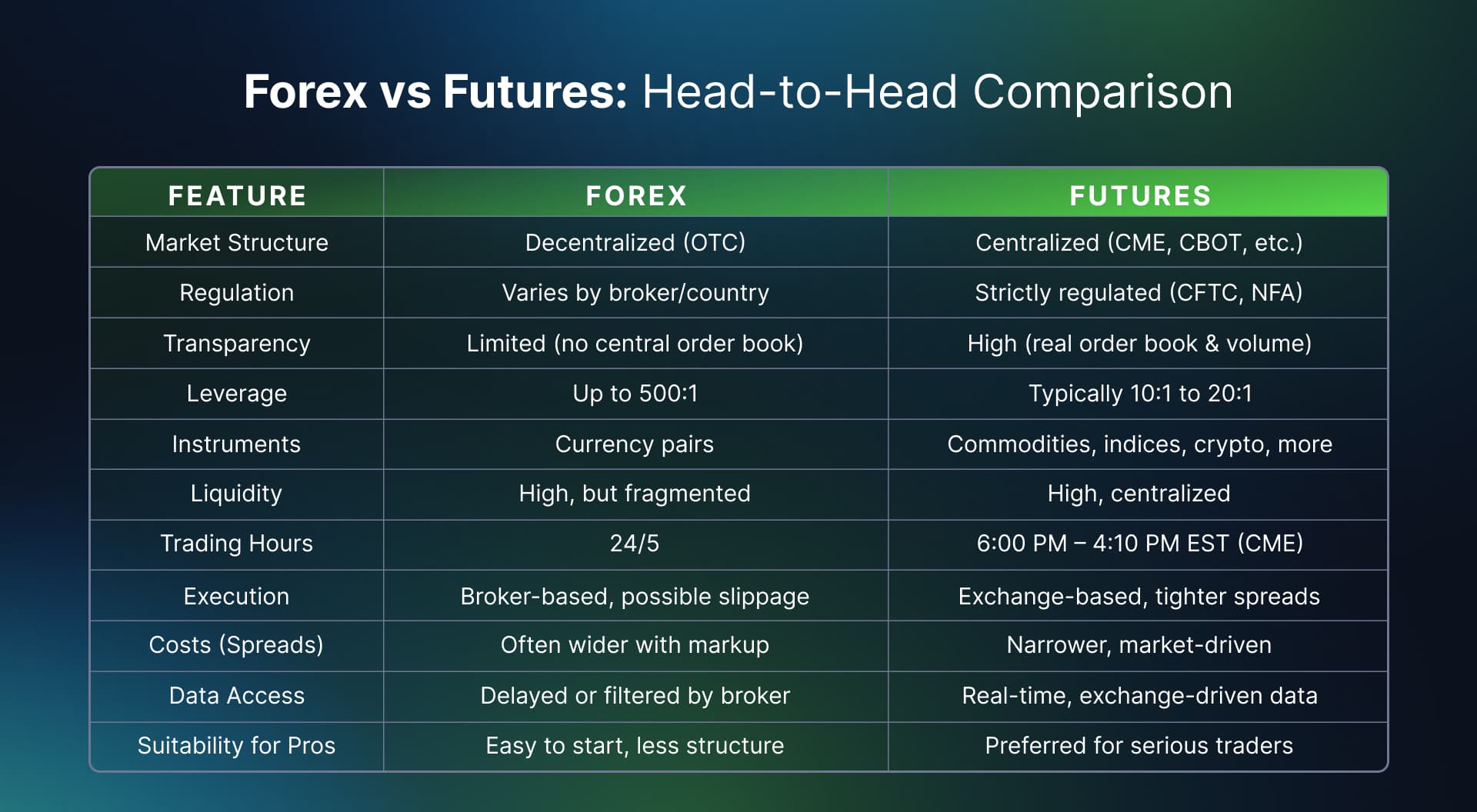 Market Access and Hours
Market Access and HoursForex: Offers nearly continuous trading from Sunday evening to Friday evening (EST), following the global financial centers around the world. This accessibility allows for flexible trading schedules.
Futures: Operates during specific exchange hours, with most liquid trading occurring during U.S. market hours for American exchanges. Many contracts offer extended electronic trading, but still with defined opening and closing times.
Liquidity and VolumeForex: The most liquid market in the world, with major pairs like EUR/USD seeing enormous daily volume. This typically results in tight spreads and minimal slippage.
Futures: Liquidity varies significantly by contract and time of day. E-mini index futures like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) offer excellent liquidity during U.S. market hours, while other contracts may have more limited liquidity windows.
Leverage and MarginForex: Typically offers higher leverage, sometimes exceeding 50:1 in offshore jurisdictions (though restricted to 50:1 in the US and lower in other regulated environments).
Futures: Margin requirements are set by exchanges and typically range from 3-12% of contract value for day trading, translating to leverage of roughly 8:1 to 30:1 depending on the instrument.
Transparency and ExecutionForex: Execution quality depends heavily on your broker. As a decentralized market, there's no single "true" price, and spreads can widen unpredictably during volatile market conditions.
Futures: All trades go through the central exchange order book, providing complete transparency in execution and pricing. Traders can see the entire order book depth with time and sales data.
Costs and FeesForex: Primarily compensates brokers through spreads (the difference between bid and ask prices), though some brokers also charge commissions. Cost structures vary widely between brokers.
Futures: Typically involves a commission per contract plus exchange and NFA fees. The pricing is generally more transparent and consistent across brokers.
Regulation and ProtectionForex: Regulatory protection varies significantly by jurisdiction. Some forex brokers operate with minimal oversight in offshore locations.
Futures: Highly regulated by entities like the CFTC and operates under exchange rules that include strict order matching protocols and segregation of client funds.
Market ParticipantsForex: dominated by large banks and financial institutions, with retail traders making up a small percentage of overall volume.
Futures: More diverse participation from hedgers, institutional traders, and retail traders, with a more transparent view of market composition through Commitment of Traders reports.
TX3 Funding: Innovating in the Futures Trading Space

TX3 Funding has emerged as a noteworthy player in the futures prop firm landscape, offering traders access to exchange-traded futures markets with several distinctive features.
Comprehensive Instrument SelectionTX3 offers access to a wide array of futures markets across major exchanges:
- CME Instruments: Including E-mini S&P 500 (ES), E-mini NASDAQ 100 (NQ), Euro FX (6E), and Micro Bitcoin (MBT)
- COMEX Instruments: Gold (GC), Silver (SI), Copper (HG), and their micro variants
- CBOT Instruments: Agricultural products like Corn (ZC) and Wheat (ZW), plus E-mini Dow Jones (YM)
- NYMEX Instruments: Energy products including Crude Oil (CL), Natural Gas (NG), and RBOB Gasoline (RB)
TX3's evaluation process focuses on realistic trading conditions:
- No minimum trading days requirement, allowing traders to trade only when genuine opportunities present themselves
- End-of-Day (EOD) trailing drawdown system that locks in at $100 above the initial starting balance
- Automatic position closing at market end (4:10 PM EST) to prevent unintentional rule violations
TX3 offers a compelling profit split structure:
- 100% of first $10,000 in profits goes directly to the trader
- 90/10 profit split thereafter (90% to trader, 10% to firm)
- Flexible payout options based on account type, with Pro Plan traders eligible for bi-weekly withdrawals
TX3 provides a structured pathway from evaluation to live trading:
- Initial Evaluation in a virtual environment to assess skills and rule adherence
- Simulated Funded Stage with virtual capital but real profit withdrawals
- Live Funded Account opportunity for consistent performers, trading with actual firm capital
Which is Right for You: Forex or Futures?
Deciding between forex and futures trading depends on several personal factors:
Consider Forex If:- You value 24-hour market access and the flexibility to trade around your schedule
- You prefer starting with smaller account sizes and position sizing
- Your trading strategy is specifically designed for currency pair dynamics and correlations
- You're comfortable conducting deep due diligence on brokers to find reliable execution partners
- You value transparency, centralized price discovery, and regulatory oversight
- Your trading approach benefits from order flow data and market depth information
- You want exposure to a diverse range of asset classes beyond currencies
- You prefer trading during structured market hours with defined sessions
- You're concerned about broker manipulation or execution quality issues
Making an Informed Decision
Both forex and futures offer viable trading opportunities but cater to different trader preferences and goals. The ideal choice depends on your trading style, capital availability, schedule flexibility, and comfort with different market structures.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap with Modern Prop Firms
While forex and futures markets have traditionally appealed to different trader profiles, innovative prop firms like TX3 Funding are bridging this gap by providing access to futures markets with accessibility features previously associated primarily with forex trading.
By offering reasonable evaluation fees, flexible trading parameters, and clear pathways to funded trading, firms like TX3 are making the regulated futures markets accessible to a broader range of traders. Start your evaluation today
Get Your Funded Account Now